Wire mesh products have become essential across a range of industries, offering both functional utility and modern aesthetics. From construction and agriculture to interior design and landscaping, mesh materials serve purposes that are as diverse as they are critical. With technological advancements and growing design demands, options such as metal grid, black wire mesh, fine wire mesh, gabion wire mesh, and architectural wire mesh are rapidly evolving to meet higher performance and visual standards.

Versatile Applications Driving Mesh Demand
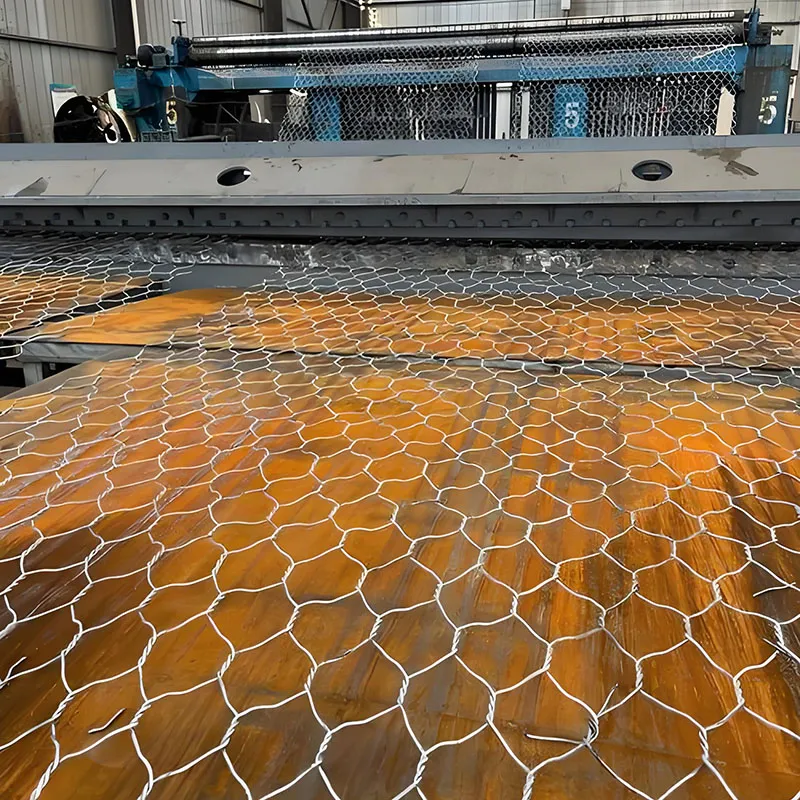
Wire mesh materials are increasingly applied in environments that demand strength, ventilation, and durability. The industrial sector relies on structured mesh configurations for everything from machinery guards to filtration systems. In recent years, metal grid products have found expanded usage in heavy-load applications such as warehouse platforms and trench covers due to their load-bearing capability and anti-slip surface texture. Similarly, black wire mesh serves a dual purpose in construction and interior spaces, offering corrosion resistance while contributing to darker, sleeker design aesthetics.
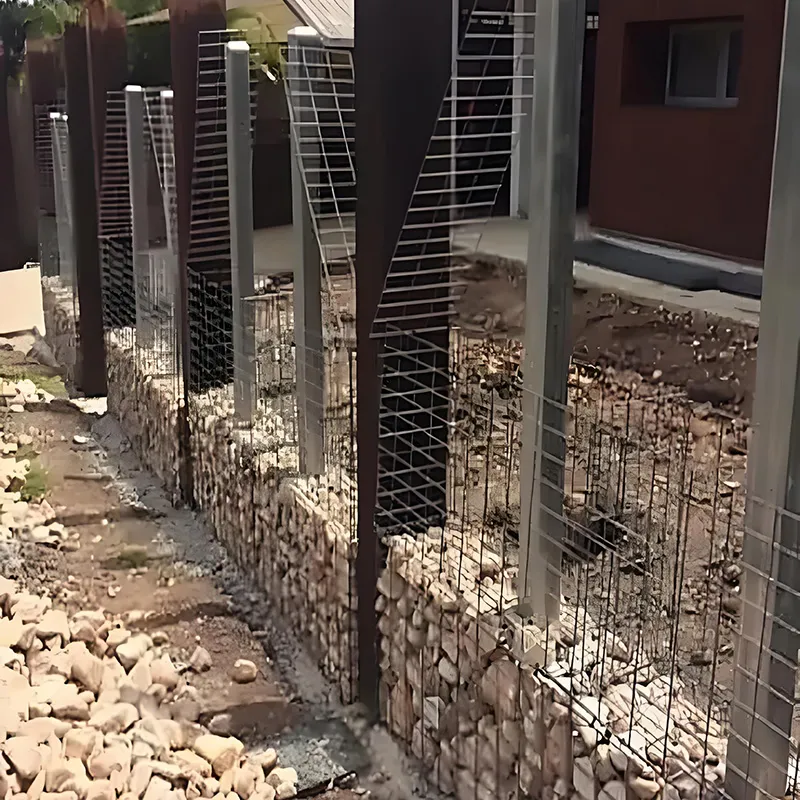
In landscaping and civil engineering, gabion wire mesh has become a preferred material for earth retention and slope stabilization. Not only is it functional, but its modular design also allows for creative expression in public and private spaces. The combination of steel strength and flexible design makes it ideal for irregular terrains and decorative boundary walls.
Precision Engineering in Fine Mesh Products
When intricate screening, sifting, or separation is needed, fine wire mesh emerges as the ideal solution. This mesh type is typically produced using stainless steel, copper, or nickel wires that are woven with high precision. Industries such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, and aerospace require extremely small apertures and uniform consistency, which fine wire mesh delivers without compromise.
Moreover, fine wire mesh is often chemically treated or surface coated to enhance resistance against corrosive environments. Its role in laboratory filters, fine sieves, and ultrasonic cleaning baskets highlights its reliability under stringent operational standards. As consumer and industrial expectations for purity and accuracy grow, suppliers are focusing on customization and digital manufacturing processes to ensure optimal performance.
Strength and Structure: The Utility of Gabions and Grids
Gabion wire mesh stands out as one of the most resilient and adaptable wire mesh systems. Constructed from galvanized or PVC-coated steel wire, it is engineered to resist rust, deformation, and pressure from soil or water. Its structural reliability makes it indispensable for retaining walls, culvert headwalls, and hydraulic works. Because gabion wire mesh can be filled with local stones or decorative materials, it also contributes to natural aesthetics while fulfilling engineering requirements.
Metal grid designs—typically forged or welded—are preferred for drainage systems, platform flooring, and walkways where airflow, water flow, and anti-slip safety are priorities. These grids are now available in modular formats, enabling faster installation and minimal maintenance in urban infrastructure projects. Clients also benefit from built-in safety margins, making metal grid options a trusted choice in high-risk industrial zones.
Merging Functionality and Design in Architecture
In contemporary architecture, wire mesh has evolved beyond a structural necessity to a defining element of visual identity. Architectural wire mesh is especially prominent in building facades, interior partitions, sunscreens, and ceiling panels. It offers an unmatched combination of light transmission, airflow, privacy, and aesthetic appeal. Fabricated from high-grade stainless steel, bronze, or aluminum, architectural wire mesh is engineered to endure outdoor conditions while retaining its finish and structural integrity.
This category of mesh allows designers to play with texture, transparency, and geometry. Whether used for a museum exterior or an office lobby divider, architectural wire mesh creates dynamic visual effects that respond to light and shadow. More importantly, it supports sustainable architecture by aiding in passive ventilation and reducing energy load. As LEED-certified designs become the new standard, architectural wire mesh is increasingly chosen for its energy efficiency and environmental benefits.

Architectural Wire Mesh FAQs
What are the key benefits of using architectural wire mesh in building design?
Architectural wire mesh combines strength with elegance, offering benefits such as ventilation, solar shading, and aesthetic versatility. It also contributes to energy efficiency and low maintenance, making it a top choice for sustainable buildings.
How is architectural wire mesh different from standard wire mesh?
Unlike standard wire mesh used for fencing or filtration, architectural wire mesh is manufactured with design intent. It uses premium metals, precise weaving or welding patterns, and surface treatments to ensure it meets both structural and visual performance standards.
Can architectural wire mesh be customized for specific projects?
Yes, architectural wire mesh is highly customizable in terms of pattern, wire diameter, material finish, and panel size. Architects and engineers often collaborate with manufacturers to create bespoke solutions tailored to the project’s environmental and visual requirements.
Is architectural wire mesh suitable for outdoor use?
Absolutely. Most architectural wire mesh products are made from stainless steel or corrosion-resistant alloys, ensuring durability even in harsh outdoor environments. Surface treatments further enhance resistance to weather and pollutants.
What installation options are available for architectural wire mesh panels?
Architectural wire mesh can be installed using frames, clamps, or cable systems, depending on the design and load-bearing needs. Some installations also include movable panels or mechanized systems for adaptive sun control or privacy.